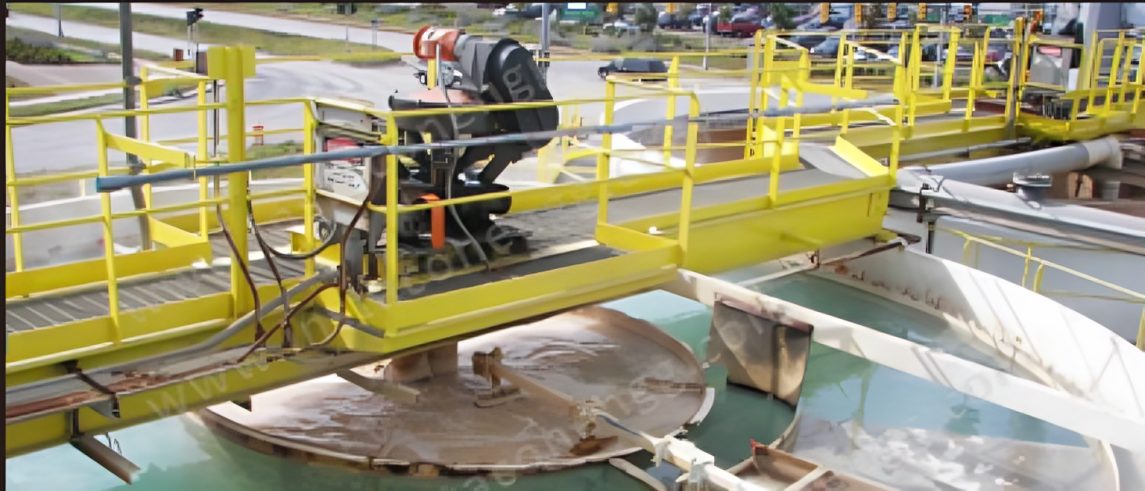
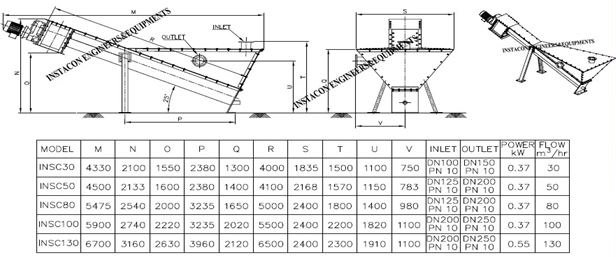
Grit Separator/ Detritor
The detritor functions as a continuous flow tank where sedimentation occurs as a result of gravity, causing the grit to settle, while the excess water flows out through outlet weirs located on the opposite side. A scraper mechanism is employed to remove the settled grit, directing it towards openings at the bottom of the sidewall. The collection chamber operates on the principle of velocity, skillfully designed to allow only grit to settle, allowing organic matter to overflow. The classifier mechanism involves a reciprocating rake, powered by a motorized gearbox. The gathered grit undergoes a thorough washing process and is then discharged from the top of the reciprocating/screw classifier through a chute for proper disposal. The washed organic liquor present in the classifier is returned to the detritor collection chamber through the organic return pump.